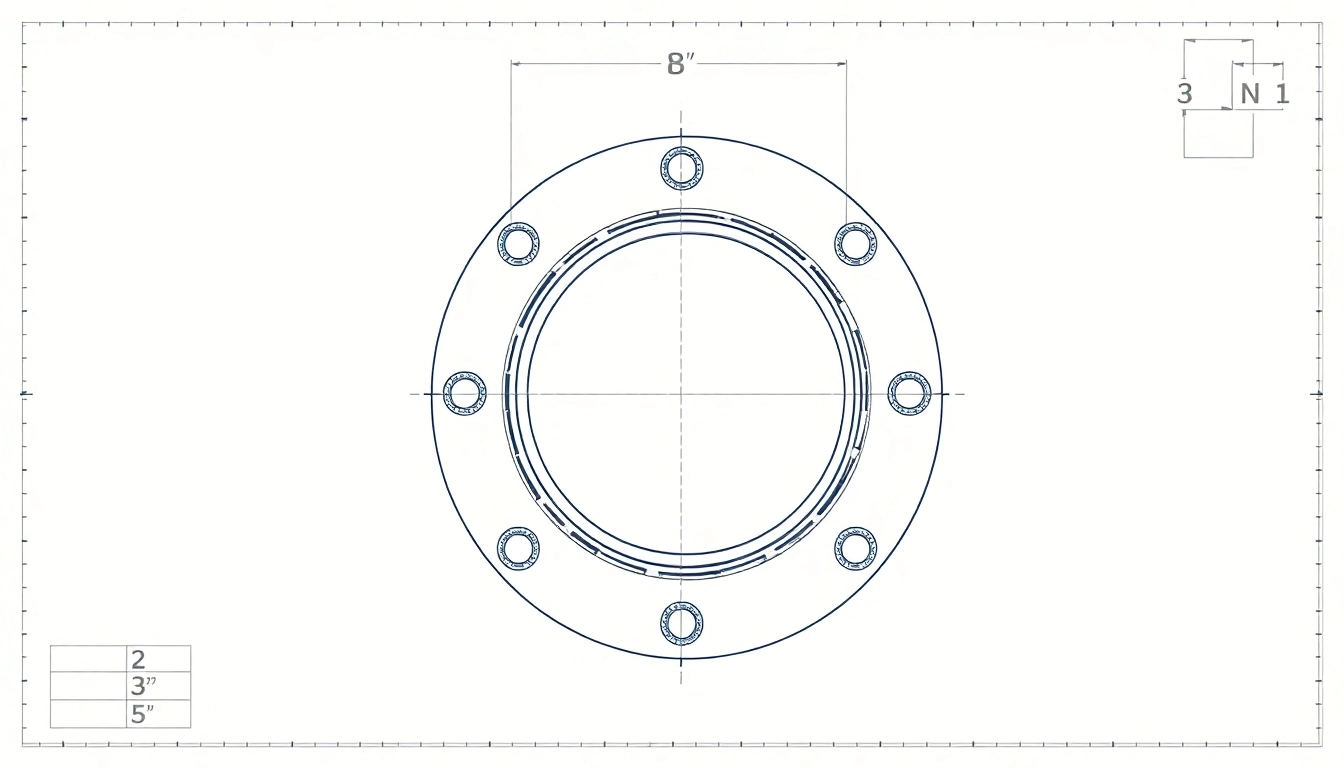
Understanding CAD Drawings for Flanges
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) has revolutionized the engineering and manufacturing landscape, particularly in the creation of precise and detailed designs. One area where CAD has shown tremendous value is in the design and production of flanges. These essential components are integral to various pipelines and systems across multiple industries, including oil and gas, construction, and automotive. Understanding cad drawings flange is crucial for engineers, architects, and designers who wish to ensure the integrity and functionality of their projects.
What Are CAD Drawings?
CAD drawings are digital representations of physical objects, made using computer software specifically designed for the creation of 2D and 3D graphics. These drawings provide comprehensive visual instructions on how to create a physical product, including dimensions, materials, and assembly processes. In engineering contexts, CAD drawings serve as blueprints, guiding manufacturers throughout the production process.
Importance of Flange Design in Engineering
Flanges play a critical role in mechanical, plumbing, and construction applications. They are used to join two components together, enabling fluid or gas transfer while maintaining integrity within a system. A well-designed flange ensures that connections are robust, leak-proof, and capable of withstanding high pressure and temperature. Thus, the precision captured in CAD drawings becomes paramount, as inaccuracies can lead to significant failures and costly repairs.
Key Concepts in CAD Drawings for Flanges
When discussing CAD drawings related to flanges, several core concepts should be understood. Key among these are:
- Dimensions: Accurate measurements dictate how flanges fit into systems.
- Material Specifications: Different materials have varying strengths and resistance to corrosion, which significantly affects flange design.
- Standardization: Familiarity with industry standards (like ANSI, ASME) is essential for ensuring compatibility between components.
- Annotation: Clear annotations in drawings facilitate proper manufacturing and assembly.
Types of Flanges and Their CAD Drawings
Common Flange Types and Applications
Flanges come in various types, each designed for specific functions and applications:
- Welding Neck Flanges: These flanges are usually used in high-pressure applications, where they help to distribute stress.
- Slip-On Flanges: Ideal for low-pressure applications, slip-on flanges are easy to install and weld.
- Blind Flanges: Employed to close a piping system or vessel, they are crucial for maintenance flexibility.
- Threaded Flanges: These are easy to install without welding, making them suitable for scenarios where welding is impractical.
- Orifice Flanges: These flanges are specifically designed to accommodate flow measurement systems.
How to Interpret Flange CAD Drawings
Interpreting flange CAD drawings requires a foundational understanding of technical drawing conventions. Important elements to focus on include:
- Projection Views: Multiple views (top, side, front) provide different perspectives.
- Cut Sections: These reveal internal features and are especially useful for complex flanges.
- Symbols and Notations: Familiarize yourself with standard symbols that indicate surface finish, tolerances, and more.
- Bill of Materials (BOM): This lists all components, including flanges, necessary for assembly.
Examples of Standard CAD Flange Drawings
Standard CAD flange drawings adhere to established guidelines and practices. Some examples include:
1. ASME B16.5 for pipe flanges and fittings
2. ASME B16.47 for large diameter flanges
3. API 605 for steel flanges
4. AWWA C207 for waterworks flanges
These standards offer templates and specifications that can streamline the design process and ensure compliance across the industry.
Creating Effective CAD Drawings for Flanges
Best Practices for Flange Drawing Creation
Creating effective CAD drawings involves adhering to several best practices:
- Start with Accurate Measurements: Always begin with precise dimensional data to ensure functionality.
- Follow Industry Standards: Utilize standardized templates to enhance compatibility and compliance.
- Use Layering Wisely: Applying different layers for various components can simplify modifications.
- Incorporate Annotations: Clear and concise notes enhance the usability of drawings for others.
- Regular Revisions: Maintain an iterative approach by continuously updating designs based on feedback and new technologies.
Tools and Software for CAD Drawings
Several tools and software programs are tailored for creating detailed CAD drawings:
- AutoCAD: Widely used for 2D and 3D design, AutoCAD is the industry standard for many engineering applications.
- SolidWorks: Preferred for 3D modeling, this software is particularly effective for complex flange designs.
- Inventor: This tool is suited for engineers requiring advanced simulation capabilities alongside CAD functionality.
- Fusion 360: An integrated solution helpful for both mechanical design and collaboration.
Troubleshooting Common Drawing Issues
While creating CAD drawings, several challenges may arise. Here are common issues and their solutions:
- Inaccurate Dimensions: Always double-check measurements against the original specification to avoid costly mistakes.
- Layer Conflicts: Utilize consistent naming conventions and organize layers meticulously.
- File Compatibility Problems: Ensure all team members are using compatible software versions, or consider exporting files in universally accepted formats.
- Software Glitches: Regularly update your CAD software and make use of the support and troubleshooting sections available.
Sharing and Collaborating on CAD Drawings
Methods for Sharing Flange CAD Designs
Effective collaboration on CAD drawings requires efficient sharing methodologies. Options include:
- Cloud Storage Solutions: Platforms like Google Drive and Dropbox provide easy access to files while allowing for version control.
- Email Attachments: While not ideal for larger files, emailing overviews for quick feedback can be useful.
- Collaboration Software: Applications like Microsoft Teams or Slack can facilitate ongoing discussions about CAD designs.
Collaborative Tools for Team Projects
When teamwork is essential in design processes, several collaborative tools help streamline communication and project management:
- CAD Collaboration Platforms: Autodesk A360 enables teams to collaborate in real time, viewing and annotating designs collectively.
- Project Management Software: Tools like Trello and Asana are excellent for managing timelines, tasks, and responsibilities.
- Video Conferencing Tools: Platforms such as Zoom or Microsoft Teams help keep teams connected during design reviews.
Ensuring Consistency Across Designs
Consistency in CAD designs must be maintained to ensure interoperability and quality:
- Developing Style Guides: A uniform style guide for CAD drawings can ensure a cohesive look across projects.
- Conducting Regular Reviews: Schedule design reviews to ensure all drawings adhere to set standards.
- Using Naming Conventions: Maintain a standardized method of naming files and layers for ease of navigation.
Future Trends in CAD Drawings for Flanges
Innovations in CAD Technologies
The future of CAD technologies is promising, showcasing several emerging trends that will enhance flange design:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) in CAD: AI tools can help automate drawing processes, identify design flaws, and suggest modifications.
- Integration of Augmented Reality (AR): AR can help visualize designs in real-time, assisting in assessments before production.
- Integration of Machine Learning: Machine learning can analyze previous designs and identify patterns for improvement in future projects.
Impact of 3D Printing on Flange Designs
3D printing is set to revolutionize how flanges are produced, offering unique advantages:
- Rapid Prototyping: Engineers can quickly produce prototype flanges to test design assumptions and make necessary adjustments.
- Design Freedom: 3D printing allows for complex geometries that would be challenging or impossible with traditional methods.
- Reduced Waste: Additive manufacturing processes utilize only the material needed for production, minimizing waste.
Adapting to Industry Changes
As industries evolve, CAD technologies and flange designs must also adapt:
- Sustainability Practices: Incorporating sustainable materials and production processes is becoming increasingly important.
- Globalization: CAD standards and practices need to adapt to international requirements as projects become more global in nature.
- Involvement of Non-Traditional Industries: Fields like biomedicine are beginning to incorporate the principles of flange design, leading to new innovations.